Полиэстер смола шога семын рӱдӧ кӱ полимер-влак, тудын универсал да кумдан шарлыше приложений дене чапланен.
Полиэстер Смола могай?
Полиэстер смола, тудын рӱдыжӧ, полимер – шинчыр повторяющийся молекулярный единице. Но мо тудым ойыртемалтше тыгыде тӱняште полимер-влак?
Определений да базовый химий .
Полиэстер смола ненасыщенный синтетике смола-влак формироватлалтеш реакций дибазный органике кислота да полигидрический спирт. Тиде тыглай вязкость, шем тӱсан жидкость. Нунын химий ӧрыктарыше, молекул куштымашым ушен, кушто кислота да спирт-влак пырля толыныт, эфир ушымашым ышташ манын.
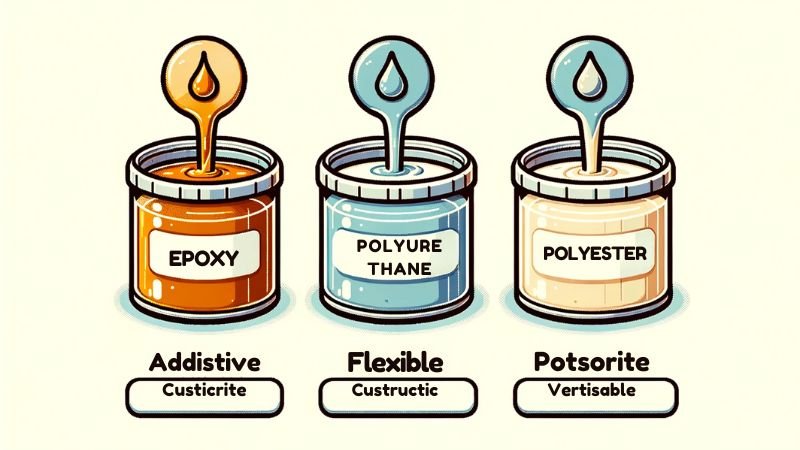
Вес смола дене таҥастарымаште .
Шуко уло гынат, нунын дене шкешотан смола, кажныже шкешотан шкешотан улмыж дене, полиэфирный смола шке вержым шке ойыртемалтше ойыртемже дене кылдалтын. Мутлан:
- Эпоксидный смола: Шке ӱлнӧ улшо клеитлымаш шкешотан да химий веществалан торешланыме дене палыме. Туге гынат, тудо тыглай полиэфир деч шергырак.
- Полиуретан смола: Предложений лывыргылык да кучылтмо приложенийыште кучылталтеш, кушто кугу абразивный торешланыше кӱлешан. Да тудын чулымлыкым вӱдыжгӧ годым эмлыме годым ограниченийым лийын кертеш.
Вашталтышым, полиэфирный смола чӱчкыдын тудын роскотлан эҥгекым ыштен, кучылташ куштылго, да тӱрлӧ приложенийлан келыштарыме.
Полиэстер смола-влакын типышт
Чыла полиэфир смола икгай огыл ышталтын. Химический умдо деч шога, ме нуным икмыняр типлан классифицироватлаш, кажныже шкешотан атрибутшо дене келыштарыме ойыртемалтше приложений.
Ортофталический смола (генеральный-целевой смола) .
Фталический ангидрид гыч лектын, тиде эн шарлыше тип полиэфирный смола пазарыште. Тиде тендан домкрат-чыла торгайыме – шот дене ак да универсал.
Свойство:
- Сай механике свойствыжым .
- Вӱдлан да тӱрлӧ химий веществалан торешланымыже .
Типичный приложений .:
- Кучылтмо стекловолокно ламинат ыштен лукмо, кузе тыгай ванна, кайык, да изи автомобиль ужаш.
Изофтолик Смола
Лӱмжым изофтал кислота гыч лектын, тиде смола шке ортофтальный иза-шольыжо ӱмбалне кугемдыме лектышым пуа.
Свойство:
- Ӱлыл вӱд ваштареш шогышо .
- Кугемдыме коррозий торешланыме ваштареш диапазон химий .
Типичный приложений .:
- Теҥыз средалан идеал, мутлан, кайык корпус-влак, нуно эреак вӱд дене лектын шогаш кӱлеш.
- Промышленный приложенийыште кучылталтше, кушто химий торешланыше приоритет.
Дициклопентадиен (ДКПД) Смола
DCPD-тиде субпродукт нафта трещинообразование. Полиэстер смола пуртымо годым, тудо икмыняр интриговатлымаш пайдам темла.
Свойство:
- Тӱшка шӧртньӧ
- Пеҥгыдылыкше да лывыргылыкшым саемдыме
Типичный приложений .:
- Автомобиль ужаш-влак, кушто лывырге пытартыш да кугу ударений торешланымаш эн тӱҥ.
- Кап панель-влак автомобильлан кӧра тудын кӱкшӧ качестван ӱмбал финишный кертмыжым.

Полиэстер смола свойствыжо-влак
Чынжымак, полиэфирный смола универсаллыкым аклаш манын, тудын шкешотан койышыжо деке ныжылгаш кӱлеш. Тиде характеристикым ойырен веле огыл, тыгак тудын келшен толмыжым рашемдаш тӱрлӧ приложений.
Механике собственность .
- Вий: Полиэстер смола-влак мокталташ лийдыме растяжка, изгибание, да сжимаемый пеҥгыдылыкым ончыктат, нуным структурный приложенийлан келшыше ыштен.
- Гибкость: Смола-влакын эн лывырге огыл гынат, нуно шке приложенийыштышт ломкость деч аралаш ситыше пуаш темлат.
- Сыранием: Ӱлыл налме годым полиэфирный смола пеҥгыде ӱмбалым ышта, тудым ешартыш да волокно дене умбакыже пеҥгыдемдаш лиеш.
Химий торешланымаш
- Чумыр: Полиэстер смола, поснак изофтолик вариант-влак, кумда спектр химий вещества торешланен, лушкыдо кислота гыч негыз марте.
- Вӱд торешланыме: Ик амалже, нунын популярностьышт теҥыз кучылтмо, полиэфир смола сай вӱд торешланен ончыкта, поснак чын формулироватлыме годым.
Пеҥгыдылыкше да илыш-йӱлаже
- УФ-ын стабилыже: Эн ультрафиолетовый стабильный огыл гынат, полиэфирный смола ешартыш дене вашталташ лиеш, кужу жап чыташ манын, кужу кече лектын.
- Чия да шинчавӱд .: Нунын механике пеҥгыдылыкыштым шотыш налын, полиэфирный смола-влак кече еда кучылтмо строгостьым чытен, лектышыш шуаш кужу жаплан продукт.
Кучылташ куштылго да универсал .
- Куринг: Полиэстер смола-влакым пӧлем температур годым эмлаш лиеш, катализатор-влакым кучылтын, мутлан, МЭКП (Метил Этил Кетон Пероксид).
- Адгезия: Нуно тӱрлӧ ӱмбаллан сайын пижыт, кумда ӱмбал ямдылыме кӱлешлыкым кораҥдаш.
- Управлений: Нунын дене пырля ыштен моштымашым темдал, пигмент, да моло ешартышым ыштен, нуным келыштарыме плетон приложений.
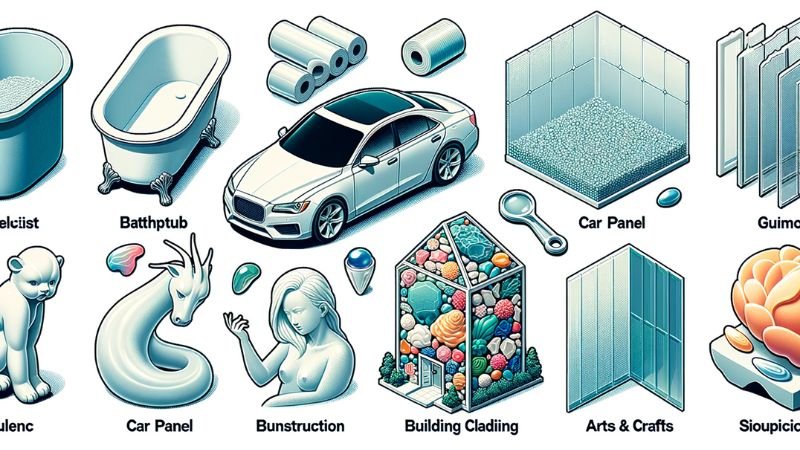
Тӱҥ приложений
Полиэстер смола’ шуко шӧрынан собственностьышто тудым тӱрлӧ отрасльыште неотъемлемый ыштен. Теҥыз судно гыч круизыш океан-влак марте пеш автомобиль ме автомобиль дене кудалыштше, тудын улмыжо повсеместный.
Теҥыз промышленность
- Кайык Халлс: Вӱд да химий торешланыме дене, полиэфир смола — кайык корпусым ыштыме тӱҥ ойырен налме, нуно эреак вӱдыштӧ эреак шинчыше-влаклан непроницаемый кодеш манын ӱшандарен.
- Дискироватлымаш & Компонент-влак: Корпус деч ӧрдыжтӧ, моло кайык ужаш гай палубо, мачта, да интерьер чӱчкыдын пашам ыштен полиэфир смола тудын пеҥгыдылыкше да обслуживатлыме куштылго.
Автомобиль
- Организмым погышо-влак: Кеч-кунам ӧрмалген, шпаклевка гай вещества кучылталтше, автомобильыште дент-влакым лывырге луктын? Тиде’ чӱчкыдын полиэфирный смола ден заполнитель-влакын мешакышт, тудын куштылгылыкшым да шлифоватлымашым куштылеммыж дене аклалтеш.
- Ламинат & Панель-влак: Шинча, лывырге тӱжвал шуко автомобиль шке лустерым полиэфирный смола дене инфузионный стекловолокно гыч ыштыме слой-влаклан парымже уло.
Конструкций
- Панель-влак & Предступлений: Зданий-влак, поснак коммерческий, полиэфирный смола негызеш панельым кучылт кертеш, эстетике да пеҥгыдылыкше.
- Ванныйыште фикс-влак: Пеҥгыде, но стильный ванна, раковина, да душ ларек, чӱчкыдын стекловолокно гыч ыштыме, нунын формо да функцийлан полиэфир смола ӱшанен.
Искусство & Ремесло
- Скульптур & Сӱретыште: Художник-влак чӱчкыдынак скульптурым ыштыме годым полиэфирный смола деке савырнат, тудын ӱпым да пытартышым акленыт.
- Ювелир ӱзгар: Смола ювелир тенденций ужын, ремесленник-влак встраивать объект да пигмент яндар полиэстер смола, ыштен ӧрыктарыше лаштык-влак.
Пайдаже да ситыдымашыже
Кеч-могай материал семынак, полиэфирный смола ӱстел деке конда, пайдам да ограниченийым мешак. Тидым пален налын кертеш, тудын йодмашыштыже информированный пунчалым лукмо йӧн дене виктарен кертеш.
Пайдаже
- Роскот-эффективность .: Ик эн тӱҥ амалже тудын кумдан кучылтмо, полиэфир смола сай балансым темлена доступен ак точко.
- Кучылтмо куштылго: Пӧлем температур да тура аралаш процедурым ыштен кертме дене, тудо’ пайдаланыше-влаклан келшыше, поснак тӱҥалше-влаклан.
- Келыштарымаш: Полиэстер смола’ тӱрлӧ ешартыш дене келшен толшо, заполнитель, да волокно тудым йӧным пуа, шуко приложений-конкретле йодмашым шукташ.
- Пырче: Тудын шкешотан пеҥгыдылыкше да торешланыше шуко экологий фактор-влак кокла шот дене ыштыме продукт дене полиэфир смола тенденций кужу ӱмыран.
- Сай адгезия: Тудын шуко ӱмбалже дене сайын кылым кучен моштымаш сложный ӱмбал ямдылыме кӱлешлыкым отрицатла.
Ситыдымашыже
- Критический: Южо моло смола дене таҥастарымаште, поснак пеҥгыдемден огыл годым, полиэстер утларак склонный лийын кертеш трещина йымалне стресс.
- UV чулымлык: Кужу жап кече волгыдо дене лектын кертеш деградировать полиэфир смола гын, тудо’ стабилизатор дене вашталтен.
- Изи шокшо торешланыме: Эпоксидный, полиэфирный смола гай материал-влак дене таҥастарымаште шокшо чытымашлан изирак порогшо уло.
- Ситарыш: Процесс годым, полиэфирный смола икмыняр шӧртньӧ ончыктен кертеш, тудо раш приложенийыште тургыжланымаш лийын кертеш.
- Прибор: Характеристикан ӱпшӧ годым эмлыме процесс лийын кертеш офф-тошто южо, поснак локтылалтше верыште.

Экологий эффект да ӱшанле .
Эра утларак да утларак рашемдыме экологий сознаний, экологий лапка материалым умылен, ме кече еда кучылтмо эн тӱҥ. Полиэстер смола, шуко отрасльыште инструментальный годым, экологий шотышто шонымашым нумалыт, тудо тӱткышым йодеш.
Экологий тургыжланымаш
- Биоразлагаемость .: Шуко синтетике полимер семынак, полиэфирный смола-влак йырым-йырысе пӱртӱсыштӧ куштылгын огыт локтылалт. Тиде кужу жаплан шӱкшакым луктеш, поснак продукций шке ӱмыржӧ мучаш марте шуэш.
- Производство лукмаш: Полиэстер смола ыштен лукмаш химий процесс-влакым ушештара, тудо загрязняющий веществам эфирыш да вӱдыш луктын кертеш.
- Волгалтарыме органике соединений-влак (ЛОС): Процесс годым, южо формулировко полиэфирный смола ЛОС луктын кертеш, тудо эҥер лавыртымашлан полша да локтылалтше верыште зияным ыштен кертеш.
Ошкыл-влак деке ӱшанле .
- Перерабатыватлыме инициативе .: Эффорт-влак полиэфирный смола гыч ыштыме продукцийым перерабатыватлаш тӱҥалыт, нуно полигонлаште огыт пытаре. Задаче-влак улыт гынат, технологийыште ончыко каяш сӧрымашым темлат.
- Био-негызеш ыштыме смола-влак: Шымлызе-влак шымлымаш смола гыч лектын, уэмдыме ресурс гыч альтернатива йӱла нефть негызеш полиэфир смола.
- Лӱдыкшӧ ВОС-ым иземдымаш .: Кызытсе формулировко да ешартыш цельым шынден, ЛОС-влакым лукмо процесс годым луктын, экологий да тазалык шотышто тургыжланымашым луштараш.
- Ответственный производствым .: Компаний-влак арулыкым ыштен лукмо йӧн-влакым илышыш пуртат, лукмашым иземдат, сырьём ӱшанле налме верлан ойыреныт.
Ончыкылык тенденций
Кузе ме писын вияҥше тӱня гоч ориентироватлаш, полиэфир смола дене пырля путешествийыш ямде, келыштарыме да инноваций. Теве’ шинчаончалтышыже, мом горизонт куча тиде универсал материал.
Технологий ончыко каяш .
- Нанотехнологий: Полиэстер смола дене нано-заполнитель-влакым пуртымо тудын койышыжым раш кугемден кертеш, механике пеҥгыдылык гыч ультрафиолетовый торешланымаш.
- Ушан материал: Шоналтыза, кайык корпусым, шкевуя паремеш изирак тыртыш але автомобиль панельым, тӱс дене вашталташ температур. Интеграций полиэфир смола дене ушан ешартыш ыштен кертеш тиде чынлык.
Экологий фокус .
- Грин Полиэстер: Эко-йолташ альтернатива деке ӱжмаш утларак кумдан шарлыше био-негызеш полиэфирный смола, ископаемый топливо деч зависимость иземеш.
- Круговой экономике: Эффорт-влак полиэфирный смола продукцийлан петыралтше системым ышташ, угыч кучылташ да утилизироватлыме деч утлаш йӧным ышташ полшат.
Кумдаҥдыме приложений скопа .
- Медицина: Биосовместимость ончыко каяш, ме медицине приложенийыште полиэфирный смола ужын кертеш, протезирование гыч медицине оборудованийым илыме вер.
- Космос да авиаций: Шымлымаш умбакыже шуйна, полиэфирный смола композит-влак аэрокосмический да космосым шымлымашын йодшо сферыште приложений-влакым муын кертыт.
Коллаборативный шымлымаш
- Промышленность-академий партнерстве: Промышленность да академический учреждений-влак коклаште сотрудничество шымлымашым писынрак ыштен, ончыко инноваций полиэфирный смола приложений да формулировко.
Мучашмут
Полиэстер смола, материал, тудо шке гыч бесшовный ургымо тӱрлӧ отрасльыште ткань, айдеме изобретательность да келыштарыме нерген танык семын шога. Тудын негызше химий гыч тӱҥалын, кумдаҥдыме приложенийже марте, тудын историйже универсал да эволюций гыч иктыже.
Тудо жапыште тудын деч посна огыл, поснак экологий ӱшанле сферыште, ончыкылык волгыдо коеш. Технологий ончыко каяш горизонт, эко-сознательный практикым кугемдыме акцент дене пырля, полиэфирный смола йӧн дене вияҥеш, умбакыже тудын пайдалыкше дене келыштарыме годым тӱнямбал ӱшанле цель дене.