Пластик инъекций формо решенийым лукмо .
Комплексный ошкыл-ошкыл-ошкыл дене ручка .
Пластикым пуртымо формо-тиде сложный да раш производствым процесс, сырьевой пластика материалым кумда спектр продукт дене сложный формо да раш габарит дене савырен.
1-ше ошкыл.
Дизайн да формо ямдылыме .
- Продуктым ыштымаш: Процесс деталь продукт дизайн але концепций дене тӱҥалеш. Проектироватлымаш шотышто функциональность, эстетике, материалым ойырен налме, да ыштен лукмо.
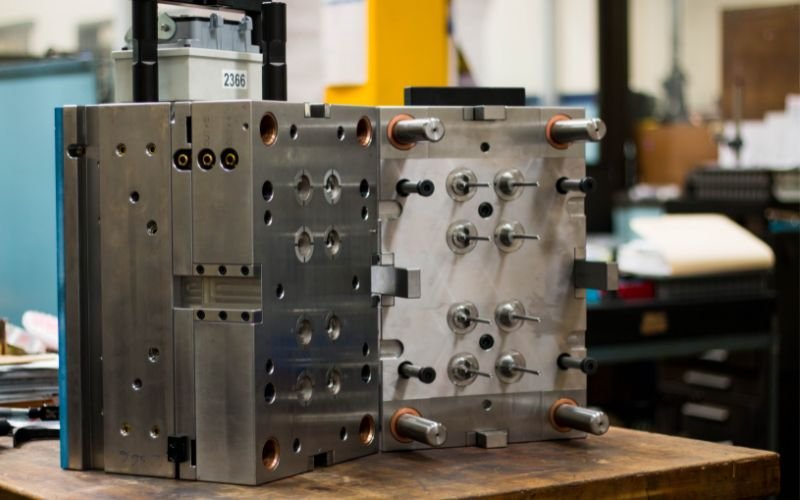
- Плесень дизайн: Плесень, тыгак ӱзгар семын палыме але колен, продукт дизайн негызеш ыштыме. Плесень кок пел гыч шога – лончо да ядро – пытартыш продуктын формыжым ыштен.
- Материалым ойырен налмаш: Ойырен налме келшыше пластика материалым негызеш продукт’ йодмаш, шотыш налын, фактор-влак гай механике шкешотан, химий торешланыше, да температур стабильность.
- Плесень Фабрикаций: Квалифицированный ӱзгар-влак ыштен лукмо формо дене пайдаланен раш обрабатыватлыше йӧн. Плесеньын сложностьшо да кугытшо ыштыме жап ден роскотлан влиянийым ышта.
Ошкыллан 2
Инъекций формо процесс .
- Зажим: Плесаным монтироваться ӱмбалне формо машина. Кок пелыжым пеҥгыдын петыреныт, гидравлический але механике вий дене пайдаланен, чын келыштарыме ӱшандарыше.
- Инъекций: Пластик пеллет, смола семын палыме, ашнаш налме вер формо машина’ бункер. Пелет-влакым шокшо да ствол кӧргыштӧ шӧртньӧ шӧртньӧ состояний марте шӧртньӧ.
- Давлений да писылык инъекций: Отношенный пластика кӱкшӧ давлений йымалне формо лончо инъекций. Плесеньым темен да тыгай ситыдымашым але раковине пале-влакым чараш манын, инъекций писылык ден давленийым виктарат.
- Йӱштӧ: Плесеньым темымеке, кӧргӧ пластика йӱштӧ да пеҥгыдемдаш тӱҥалеш. Йӱштӧ жапым тыматлын контрольышто кучаш кӱлеш ужаш качествыжым шукташ.
- Давленийым кучен: Южо формо-влак коклаште йӱштӧ годым материальный шӧртньӧ компенсацийым кучаш давленийым куча. Тиде ужаш шке формыжым да габаритшым арален кода.
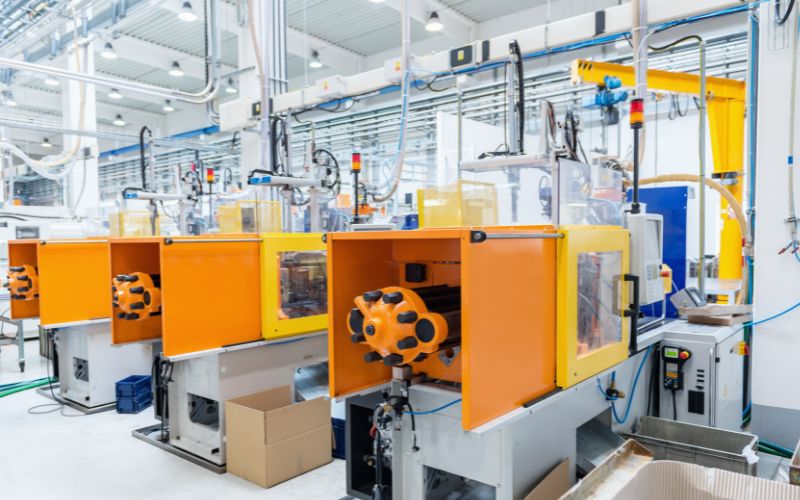
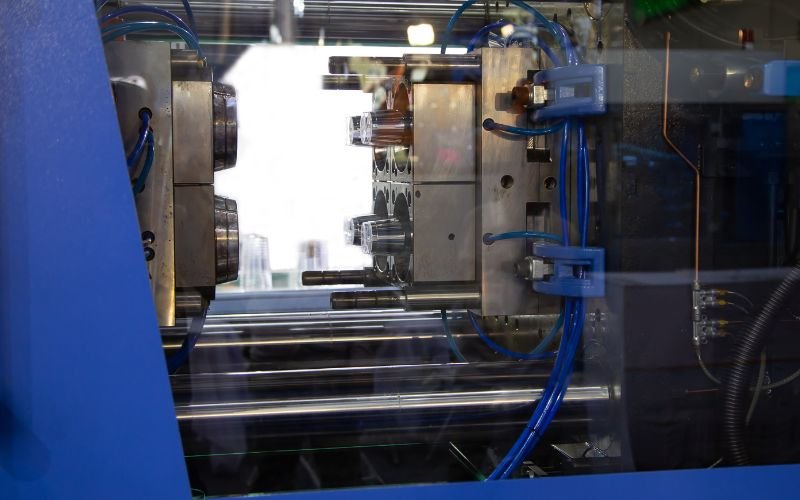


Ошкыллан 3 .
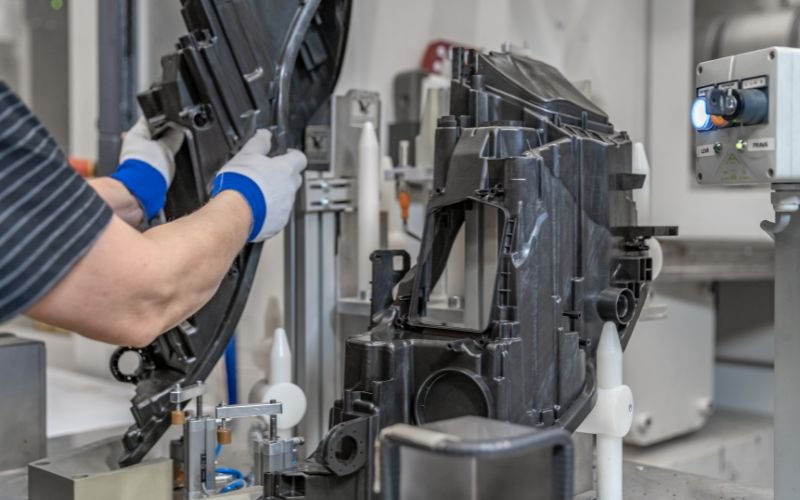
Плесеньым почмо да лукмо .
- Йӱштӧ пашам пытарыме: Пластик ситышын йӱштӧ да пеҥгыдемдыме деч вара, формо почылтеш, кӧргыштӧ пеҥгыдемдыме ужашым почын пуа.
- Эжекций: Плесень эжектор пин-влак формо лончо гыч ужашыжым луктын шупшыт. Эжекция ласкан лийшаш, утлаш манын, ужаш’ ӱмбал зияным ыштен.
Ошкыллан 4
Послеродный-процессирующий .
- Тримминг да Дефлаш: Уто материал, флэш маналтеш, ужаш гыч кораҥдалтеш. Пытартыш формым шукташлан кид дене ыштыме але автоматизироватлыме процесс-влак лийыныт.
- Кокымшо операций: Продукт деч шога’ йодмаш, ешартыш процесс гай бурильный, обрабатыватлыше, але чумырген кертеш.


Ошкыллан 5
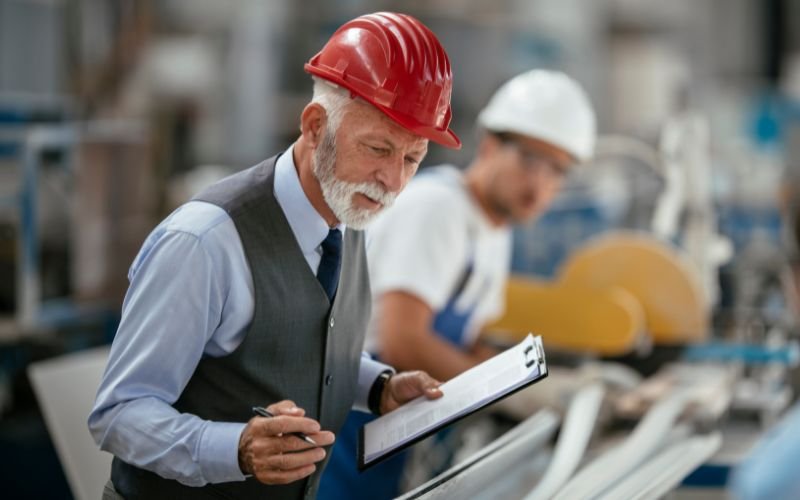
Качествым тергымаш да тергымаш
- Визуальный тергымаш: Кажне ужашыжым визуально тергымаш дефект, кузе тыгай ӱмбал несовершенство, тӱс несоответствий, але искажение.
- Грудалык тергымаш: Частный висалтын да дене таҥастарымаште спецификация дизайныште ончыктымо. Ончыл висымаште оборудованийым ӱшандарыше чынлык.
6-шо ошкыл.
Упаковочный да колтымо .
- Упаковочный: Пытартыш ужаш-влакым транспортироватлымаш годым эҥгекым ышташ огыл манын, тыматлын оптат.
- Намиен: Частный клиент але монтаж объектыш колтымо интеграцийлан кугурак продукцийым але шеледымаш мучаш пайдаланыше-влаклан.

