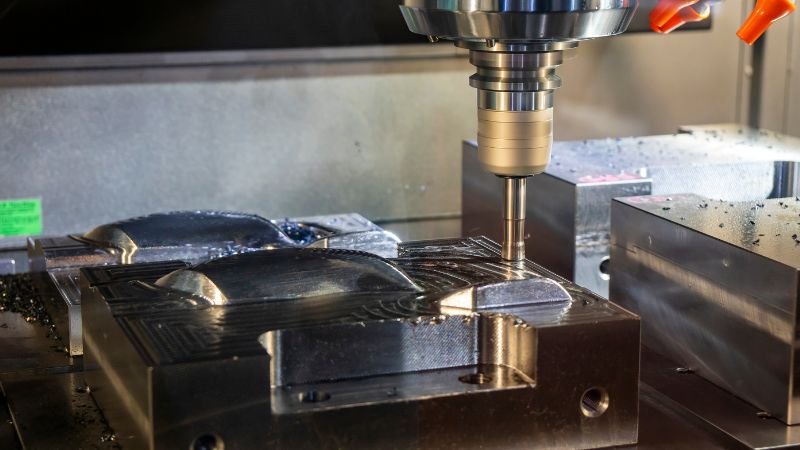
Intshayelelo
Precision injection mold making is crucial for manufacturing, demanding a blend of technology and craftsmanship. It’s vital for small, intricate products, where every detail relies on meticulous mold design and manufacturing. Precision molds ensure consistent quality, particularly in aerospace, medical, and electronics, where even minor flaws can lead to significant issues.

What is Precision Injection Mold Making?
Precision injection mold making combines metallurgy, mechanics, and careful craftsmanship to create accurate molds used for producing components through injection molding. Unlike regular molds focused on mass production, precision molds prioritize accuracy and attention to detail. They are essential for high-stakes industries where precision is critical.
Defining Precision
Precision, in the context of mold making, transcends mere accuracy. It encapsulates the mold’s ability to:
- Replicate: Faithfully mirror the original design in every produced part.
- Sustain: Maintain exactness over numerous production cycles.
- Consist: Ensure every part produced is indistinguishable from its peers in dimension and quality.
A Stark Contrast to Standard Mold Making
Comparatively, precision molds and standard molds differ vastly in the following realms:
- Tolerances: Precision molds abide by exceedingly tight tolerances, sometimes down to a few micrometers, ensuring the produced parts are flawlessly consistent and align with the design specifications.
- Complexity: The capacity to materialize intricate designs, multifaceted geometries, and complex features is a hallmark of precision mold making.
- Investment: Both in terms of time and resources, precision molds necessitate a heightened investment, aligning with their output quality and durability.
Industries Relying on Precision Molding
Medical, aerospace, electronics, and more – numerous sectors pivot on the prowess of precision molds:
- Izixhobo zonyango: Precision molds dictate the reliability of countless medical devices, where even a microscopic discrepancy could be detrimental.
- Aerospace Components: Ensuring components are lightweight yet uncompromisingly robust and accurate, precision molds play a pivotal role in aerospace manufacturing.
- Electronics: As electronics miniaturize while becoming more complex, precision molds enable the production of compact, detailed, and reliable components.

Materials in Precision Mold Making
In precision injection mold making, materials are more than just the base. They play a crucial role, connecting design accuracy and durability, ensuring the mold can consistently produce many parts without losing accuracy or wearing out.
Essential Characteristics of Mold Materials
Selecting an appropriate material for precision mold making is entwined with recognizing and balancing numerous properties, ensuring the mold can:
- Withstand Pressure: Endure the immense injection pressures without deformation.
- Resist Wear: Maintain integrity and detail across countless cycles.
- Manage Thermal Dynamics: Facilitate efficient cooling and withstand thermal cycling.
Steel Versus Aluminum: A Calculated Choice
Steel and Aluminum emerge as prevalent contenders in mold materials, each harboring their respective advantages and constraints.
Steel Molds
Pros:
- Superior wear resistance
- Extensive life cycle
- Excellent surface finish capabilities
Cons:
- Higher initial cost
- Potentially longer lead times
Aluminum Molds
Pros:
- Faster machining
- Excellent thermal conductivity
- Lower cost
Cons:
- Potentially limited life cycle
- Imiba enokwenzeka yokunxiba kwiimeko ezinomthamo ophezulu
Iingubo kunye noNyango: Ukuphucula ukusebenza kweMold
Ngaphandle kweepropathi zezinto eziphathekayo, iingubo kunye nonyango zisebenza ukukhulisa ukusebenza komngundo, ukwazisa ukongezwa:
- Nxiba ukuxhathisa: Ukwandiswa kokuqina kokungunda ngokuchasene nemathiriyeli yokurhawuka.
- Ukuxhathisa ukonakala: Ukukhuselwa kumhlwa onokuthi uvele kwiiplastiki ezithile okanye kwiinkqubo zokupholisa umngundo.
- NONE Ukuququzelela ukukhutshwa okulula kwenxalenye yokugqibela, ukunciphisa umngcipheko weziphene.
Ukurisayikilisha kunye noZinzo
Kwihlabathi elizingise kuqheliselo oluzinzileyo, ukusetyenzwa ngokutsha kunye nobuhlobo bendalo bezinto zokungunda ziye zagxila kwizinto ezibalulekileyo, ezibandakanya:
- Ukusetyenziswa kwezinto: Ukunciphisa inkunkuma ngexesha lokwenziwa kokungunda.
- Ukupheliswa koBomi kwakhona: Ukuqinisekisa ukubumba kungaphinda kusetyenziswe emva kokusetyenziswa.
- Iinkqubo ezihambelana ne-Eco: Ukusebenzisa iindlela zokwenziwa kwemveliso ezithathela ingqalelo iimpembelelo zokusingqongileyo.
IiTeknikhi zoBuchule boBuchule boBuchule
Ukubumba okuchanekileyo akwenziwanga nje ukuyilwa, kuyilwe ngobuchule, kufuna i-symphony yeendlela eziphambili zobuchule bokuzisa uyilo oluntsonkothileyo, oluchanekileyo kwinyani ebambekayo.
CNC Machining
IComputer Numerical Control (CNC) Machining, i-linchpin yokubumba ngokuchanekileyo, yenza ngokuzenzekelayo ukuguqulwa koyilo lwedijithali kwizinto eziphathekayo, ukuqinisekisa:
- Ukungaguquguquki: Ukuphindaphinda okungagungqiyo kwimijikelo emininzi yemveliso.
- Ukuchaneka: Ukubambelela kunyamezelo olungqongqo olungaphakathi ekwenzeni umngundo ochanekileyo.
- Ulawulo oluntsonkothileyo: Ukuququzelela ukufezekiswa koyilo oluntsonkothileyo kunye neejometri.
Umatshini wokukhupha uMbane (EDM)
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), or spark machining, empowers mold makers to carve minute, detailed features with supreme accuracy, focusing on:
- Fine Details: Generating micro-features and intricate details otherwise challenging through conventional machining.
- Surface Quality: Offering excellent surface finishes, crucial for both aesthetic and functional aspects of molded parts.
- Hard Material Machining: Enabling machining of hardened mold materials without inducing stress.
High-Speed Machining (HSM)
Balancing the delicacy of precision with the expediency of production, High-Speed Machining (HSM) emerges as a key player in:
- Reduced Lead Times: Amplifying production speed without compromising on precision.
- Ukugqitywa komphezulu ophuculweyo: Ukunciphisa ukupolisha ngesandla ngokuqinisekisa umgangatho ophezulu owenziwe ngoomatshini.
- Ubomi obude besixhobo: Ukunciphisa ukunxiba kwizixhobo zoomatshini ngenxa yemikhosi esezantsi yokusika.
5-Axis Machining
I-5-Axis Machining pivots ekukwazini kwayo ukuhambahamba ngeeaxes ezintlanu ezahlukeneyo ngaxeshanye, ivula:
- Ukufezekiswa kweJiyometri entsonkothileyo: Ukuxhobisa abenzi bokubumba ukuba bakhe iifom ezintsonkothileyo, ezinamacala amaninzi.
- Ukufikeleleka kwesixhobo: Ukuvumela ukufikelela kwiifitsha zecandelo elingumngeni kunye neendlela ezisezantsi.
- Ukucwangcisa okukodwa: Ukunciphisa amaxesha okuseta kunye neempazamo ezinokwenzeka ngokuququzelela umatshini obanzi kulungiselelo olunye.
Ukudibanisa i-Automation
Ukuzenzekela ekwenzeni ubumba obuchanekileyo abuyonto ilula kodwa iyimfuneko, iqinisekisa:
- Imveliso ye-24/7: Ukwandisa imveliso ngokuququzelela umjikelezo wemveliso oqhubekayo, ongajongwanga.
- Minimized Human Error: Sustaining consistency and accuracy across every mold produced.
- Resource Optimization: Efficiently utilizing materials and energy, aligning with sustainable manufacturing practices.
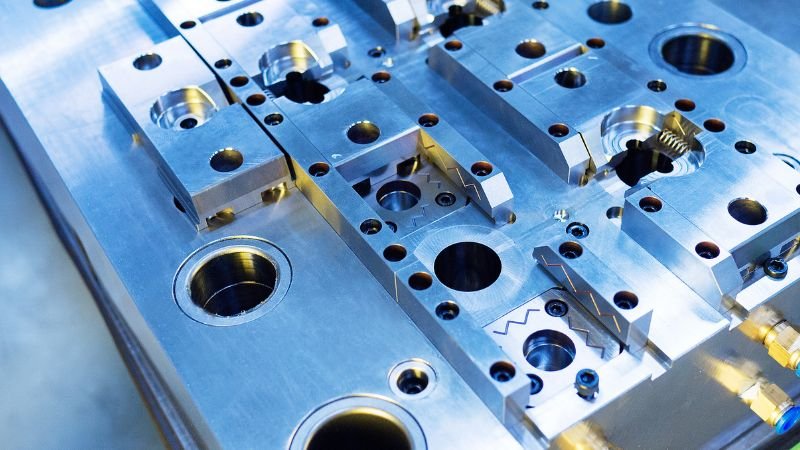

Engineering Tight Tolerances
Maintaining strict tolerances in precision injection mold making goes beyond typical engineering practices, entering a realm where every tiny measurement, down to the micron, can determine success or failure.
Defining Tolerances in Precision Molding
In the context of precision molds, tolerances refer to the permissible variance in the dimensional attributes of the manufactured part. Defining and adhering to these limits ensure that:
- Fit: Components seamlessly integrate into assemblies.
- Function: Parts perform optimally without mechanical hindrances.
- Form: Aesthetic and ergonomic integrity is preserved.
Techniques to Achieve Tight Tolerances
- Precision Machining: Employing advanced machining tactics, like 5-axis and high-speed machining, which facilitate the achievement and consistency of tight tolerances.
- Optimal Material Selection: Choosing materials that not only withstand rigorous use but also remain dimensionally stable through varied thermal and pressure cycles.
- Tooling Precision: Ensuring the tools utilized for machining are meticulously crafted and maintained to prevent dimensional discrepancies in mold creation.
Challenges in Maintaining Microscopic Tolerances
Ensuring and maintaining tolerances within a few micrometers presents a slew of challenges:
- Material Behavior: Managing the nuances of how materials expand, contract, and warp under diverse operating conditions.
- Machining Stability: Maintaining unerring stability and precision across extensive and repeated machining cycles.
- Wear and Tear: Counteracting the subtle, yet accumulatively significant, impact of wear on tools and molds.
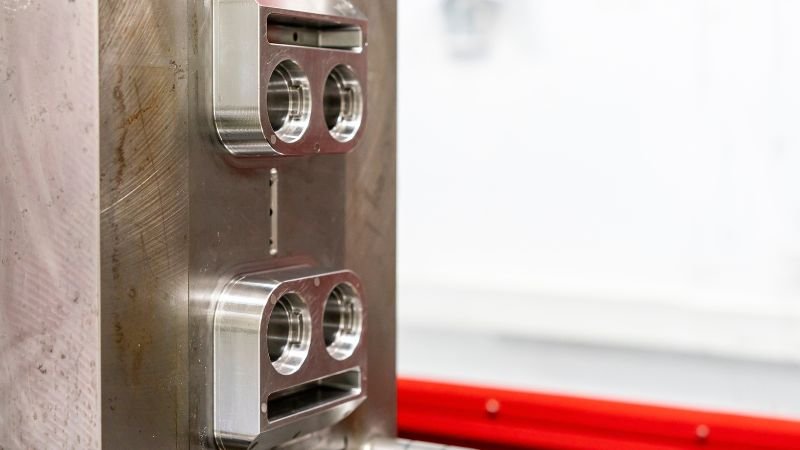

Ulawulo lwemeko & Inspection
In the complex realm of precision injection mold making, it is crucial to ensure that each mold meets specified specifications and quality standards.
The Imperative of Precision
- Microscopic Tolerances: Understanding and managing the challenges of maintaining precision within microscopic tolerances.
- Impembelelo ethe ngqo kwiiMveliso zokuGqibela: Ukuqaphela ukuba ukuchaneka kwe-molds kuguqulela ngokuthe ngqo kumgangatho kunye nokusebenza kwezinto ezenziweyo.
IiProthokholi zoLawulo loMgangatho
- Ukuqinisekiswa koYilo: Ukuqinisekisa ukuba uyilo lokungunda lomelele kwaye lubambelela kwithiyori kunye nokusebenza okusebenzayo.
- Ukuqinisekiswa kweMathiriyeli: Ukuqinisekisa ukuba izinto ezisetyenziselwa ukwenza umngundo zihambelana nemigangatho echaziweyo kwaye zifanelekile kwizicelo ezijoliswe kuzo.
- Ukuqinisekiswa kweNkqubo: Ukubekwa kweliso okuqhubekayo kwenkqubo yokwenza umngundo ukuqinisekisa ukuthotyelwa kwemigaqo emiselweyo kunye nebenchmarks.
UbuChwephesha bokuHlola kunye nobuChwephesha
- Ukuhlolwa okubonakalayo: Ukuthumela amagcisa anezakhono ukwenza uhlolo olucacileyo lwembonakalo kumanqanaba ahlukeneyo enkqubo yokwenza umngundo.
- Technological Aids: Implementing technologies like Computer-Aided Inspection (CAI) and Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) to enhance inspection accuracy.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Employing techniques such as ultrasonic testing and X-ray testing to inspect molds without causing any damage or alteration.
Addressing and Rectifying Deficiencies
- Correction Protocols: Implementing standardized procedures to address and rectify identified deficiencies during inspections.
- Root Cause Analysis: Deploying methodologies to identify and address the root causes of issues, preventing their recurrence.
- Continuous Improvement: Engaging in an ongoing process of feedback, correction, and improvement to enhance overall quality and efficiency.
Documentation and Compliance
- Quality Documentation: Meticulously documenting quality control and inspection processes, findings, and corrective actions.
- Compliance Verification: Ensuring that all quality control and inspection processes comply with relevant local, national, and international standards.
- Audit Preparedness: Maintaining readiness for internal and external audits to validate the effectiveness and compliance of quality control processes.
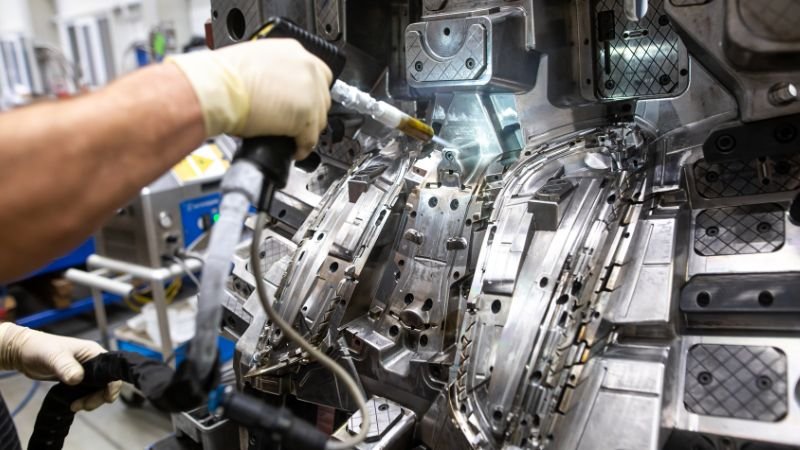

Uhlalutyo lokuhamba kokungunda & Design Optimization
Exploring the technical aspects of mold creation, mold flow analysis, and design optimization emerge as critical stages. It’s essential to ensure that molten material flows optimally through the mold and that the design is refined for both efficiency and quality.
Fundamentals of Mold Flow Analysis
- Purpose and Importance: Unraveling why mold flow analysis is integral in anticipating potential manufacturing challenges.
- Simulation Technologies: Employing advanced simulation tools to visualize material flow, identify potential issues, and formulate solutions.
- Data Analysis: Analyzing data from simulations to comprehend the intricate dynamics of material flow within the mold.
Identifying Flow-Related Challenges
- Weld Lines and Air Traps: Detecting areas prone to forming weld lines and air traps which can compromise product integrity.
- Shear Stress: Analyzing regions of high shear stress which may affect material properties and product quality.
- Cooling Inconsistencies: Identifying potential inconsistencies in cooling which can lead to deformations and quality issues.
Design Optimization Strategies
- Iterative Design: Adopting an iterative approach, continually refining the mold design based on flow analysis insights.
- Balancing Aesthetics and Functionality: Striking a delicate balance between maintaining aesthetic appeal and ensuring functional reliability of the final product.
- Material Efficiency: Optimizing design to ensure minimal material usage while preserving product quality and functionality.
Material Selection and its Impact on Flow
- Material Characteristics: Understanding how different material properties (like viscosity, thermal conductivity, etc.) influence flow within the mold.
- Material-Design Synchronization: Ensuring the mold design is tailored to accommodate and optimize the characteristics of the chosen material.
Integrating Feedback for Continuous Improvement
- Utilizing Real-world Data: Incorporating insights and data derived from actual production runs to further refine mold designs.
- Adaptive Design Models: Employing adaptive models that can be modified and optimized as per evolving requirements and technological advancements.
- Cross-Project Learnings: Applying learnings and insights from one project to anticipate and navigate challenges in future endeavors.

Advanced Technologies and Future Perspectives
The journey of precision mold making is continually evolving, shaped by the ongoing wave of technological advancements and innovative perspectives that are shaping the future of manufacturing.
Incorporating Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence is steadily infiltrating the realms of mold making by:
- Predictive Maintenance: Utilizing AI to anticipate and preemptively address machine and mold maintenance needs, minimizing unplanned downtimes and ensuring sustained precision.
- Quality Assurance: Employing intelligent algorithms to scrutinize and assure quality adherence throughout the mold-making process.
- Process Optimization: Analyzing real-time data to dynamically optimize the manufacturing process, enhancing efficiency and output quality.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive Manufacturing, or 3D Printing, pioneers new horizons by:
- Rapid Prototyping: Accelerating the mold design and testing phases through swift, cost-effective prototype creation.
- Customization: Empowering manufacturers to cost-effectively produce customized molds for short-run productions or bespoke applications.
- Ukwenziwa kweJiyometri entsonkothileyo: Ukwenza ukuveliswa kokungunda ngeejometri ezintsonkothileyo ezinomngeni okanye ezingenakwenzeka ukuvelisa kusetyenziswa iindlela zesintu.
Ukubandakanya i-Intanethi yezinto (IoT)
I-Intanethi yeZinto (IoT) idibanisa iindawo ezibonakalayo kunye nedijithali, izisa:
- Ukubekw'esweni okukude: Ukuququzelela ukujonga ngexesha lokwenyani lenkqubo yokwenza umngundo naphi na, ukuqinisekisa ulongamelo oluqhubekayo kunye nongenelelo olukhawulezileyo xa kufuneka.
- Izigqibo eziqhutywa yiData: Ukusebenzisa amandla edatha edityanisiweyo ukwenza izigqibo ezizizo ezandisa ukusebenza kakuhle
, umgangatho, kunye nozinzo.
- Uhlalutyo oluqikelelweyo: Ukusetyenziswa kwedatha ye-IoT ukuqikelela nokuthintela imiba enokwenzeka, ukukhuthaza indlela esebenzayo yokwenza umngundo.
Uhlaza kunye neZenzo eziZinzileyo
An increasing focus on environmental sustainability ushers in practices that encompass:
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Exploring and adopting mold materials that are biodegradable or made from recycled sources.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient manufacturing processes and equipment.
- Waste Reduction: Minimizing waste generation during mold making and end-of-life recycling of molds.
Ukuqukumbela
Ukwenziwa kokungunda okuchanekileyo kukudityaniswa kobugcisa kweenkcukacha ezichuliweyo kunye nokuchaneka kwezenzululwazi, ukuqhuba ukuveliswa kwezinto ezintsha kuwo wonke amashishini afana nezempilo, i-aerospace, i-electronics, kunye neemoto. Isebenza ngokuzolileyo emva kwemiboniso, ilungisa ubomi bethu bemihla ngemihla. Ukujonga phambili, kuya kuvela ngakumbi, ukusebenzisa i-AI, ushicilelo lwe-3D, i-IoT, kunye nozinzo lokuchaza kwakhona okunokwenzeka. Ukuchaneka akuwona nje umgangatho, yibha ehlala inyuka, kwaye umgangatho awugungqi. Ukwenza inaliti yokungunda echanekileyo iquka ubuchule bomntu, ukuma mde kwihlabathi apho nezona nkcukacha zincinci zibambe amandla obukhulu.