Введение
Представьте себе прозрачную пластиковую бутылку, в которой хранится ваш любимый напиток, яркую одежду из полиэстера, которую вы носите, или даже прочные волокна, используемые в автомобильных компонентах. Скорее всего, ПЭТ принимает непосредственное участие в создании этих предметов повседневного использования. Но что такое ПЭТ и почему он так важен в мире пластмасс?
Раздел 1: Общие сведения о полиэтилентерефталате
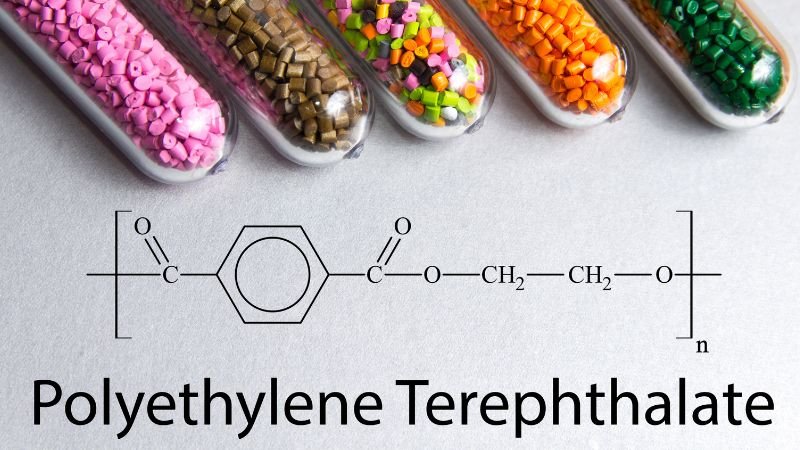
Полиэтилентерефталат, или ПЭТ, представляет собой универсальный и широко используемый термопластичный полимер, который оставил неизгладимый след в различных отраслях промышленности и аспектах нашей жизни. Чтобы по-настоящему оценить его значение, давайте углубимся в то, что такое ПЭТ и что делает его предпочтительным материалом для множества применений.

1.1 Химия ПЭТ
По своей сути ПЭТ представляет собой синтетический полимер, состоящий из повторяющихся звеньев двух мономеров: этиленгликоля и терефталевой кислоты. Эта химическая структура отвечает за многие замечательные свойства ПЭТ. Он образует длинноцепочечный полимер с высокой степенью кристалличности, что способствует его прочности и долговечности. Сочетание атомов кислорода, углерода и водорода в молекулярном составе ПЭТ придает ему легкий и прозрачный характер, что делает его идеальным для различных применений.
1.2 Краткая история ПЭТ
История ПЭТ восходит к середине 20-го века, когда он был впервые синтезирован и запатентован в Соединенном Королевстве Уинфилдом и Диксоном в 1941 году. Первоначально ПЭТ разрабатывался как текстильное волокно, известное как “Терилен” или “Дакрон,” набирает популярность благодаря устойчивости к морщинам и простоте ухода. Со временем область применения ПЭТ вышла далеко за пределы текстиля, укрепив его роль универсального пластика.
1.3 ПЭТ: материал для современной жизни
Что отличает ПЭТ, так это его адаптируемость и широкий спектр применения. Он стал важным материалом в различных отраслях промышленности, в том числе:
- Упаковка: прозрачность, барьерные свойства и легкий вес ПЭТ делают его идеальным выбором для бутылок для напитков, пищевых контейнеров и блистерной упаковки.
- Текстиль: полиэфирное волокно ПЭТ используется для изготовления одежды, ковров и обивки благодаря своей долговечности, устойчивости к морщинам и стойкости цвета.
- Автомобильная промышленность: ПЭТ встречается в салонах автомобилей, тканях сидений и компонентах под капотом, где его прочность и термостойкость проявляются.
- Электроника: ПЭТ-пленки используются в электронных дисплеях, конденсаторах и изоляционных материалах.
- Медицинский: ПЭТ используется в медицинских устройствах, таких как пакеты для внутривенного вливания и трубки, благодаря его биосовместимости и простоте стерилизации.

Раздел 2: Свойства ПЭТ
Полиэтилентерефталат (ПЭТ) — замечательный пластик с богатым набором свойств, которые делают его бесценным материалом в различных областях применения.
2.1 Прочность и долговечность
ПЭТ обладает превосходной прочностью на разрыв, что делает его одним из самых прочных термопластов. Это означает, что он может выдерживать значительные механические нагрузки, не деформируясь и не ломаясь. Независимо от того, используется ли ПЭТ в бутылках для напитков или в автомобильных компонентах, прочность ПЭТ обеспечивает долговечность продукции.
2.2 Прозрачность и ясность
Одним из наиболее ярких качеств ПЭТ является его прозрачность. ПЭТ исключительно прозрачен, что позволяет потребителям видеть содержимое бутылки или яркие цвета упаковки на основе ПЭТ. Это свойство важно для таких продуктов, как бутылки для воды и безалкогольных напитков, где визуальная привлекательность содержимого имеет решающее значение.
2.3 Легкая природа
ПЭТ — легкий материал, который особенно полезен в упаковочной промышленности. Его низкая плотность не только снижает затраты на транспортировку, но и способствует снижению выбросов углекислого газа. Легкий вес ПЭТ играет ключевую роль в снижении потребления энергии во время транспортировки.
2.4 Барьерные свойства
Барьерные свойства ПЭТ проявляются в упаковке. Он эффективно предотвращает проникновение кислорода, углекислого газа и влаги, сохраняя свежесть и срок годности продуктов питания и напитков.
2.5 Пригодность к вторичной переработке
Возможно, одной из самых знаменитых особенностей ПЭТ является его возможность вторичной переработки. ПЭТ подлежит вторичной переработке, а переработанный ПЭТ (rPET) используется для создания новых продуктов, снижая воздействие на окружающую среду и продвигая экономику замкнутого цикла.

Раздел 3: Производственный процесс
Путь полиэтилентерефталата (ПЭТ) от сырья до известного нам универсального материала является свидетельством точного машиностроения и химического синтеза. В этом разделе мы углубимся в тонкости процесса производства ПЭТ.
3.1 Полимеризация: создание ПЭТ-смолы
Производство ПЭТ начинается с процесса, называемого полимеризацией. Эта химическая реакция предполагает соединение двух ее основных компонентов: этиленгликоля и терефталевой кислоты. В результате получается прозрачная и вязкая жидкость, известная как бис(2-гидроксиэтил)терефталат или BHET. Альтернативно, ПЭТ-смола также может быть синтезирована непосредственно с использованием диметилтерефталата (ДМТ) и этиленгликоля.
Процесс полимеризации обычно включает в себя следующие этапы:
- Этерификация: Терефталевая кислота и этиленгликоль соединяются в реакторе, образуя BHET.
- Поликонденсация: Дальнейшее нагревание и вакуумирование удаляют избыток этиленгликоля, создавая высокомолекулярный ПЭТ.
3.2 Переработка расплава: преобразование смолы в продукты
ПЭТ-смола в форме небольших гранул или гранул преобразуется в различные продукты путем обработки расплава. Ключевые методы включают в себя:
- Литье под давлением: Плавление гранул ПЭТ-смолы и впрыскивание расплавленного материала в формы позволяет получить широкий ассортимент продукции: от крышек для бутылок до сложных автомобильных компонентов.
- Экструзия: ПЭТ-смола плавится и пропускается через матрицу для создания непрерывных форм, таких как пластиковые пленки, листы и профили.
- Выдувное формование: Для полых предметов, таких как бутылки, ПЭТ плавится и выдувается в форму, чтобы принять желаемую форму.
3.3 Контроль качества при производстве ПЭТ
Контроль качества имеет первостепенное значение при производстве ПЭТ, поскольку позволяет гарантировать, что материал соответствует строгим спецификациям для различных применений. Ключевые аспекты включают в себя:
- Контроль вязкости: Точный контроль вязкости ПЭТ позволяет добиться желаемых свойств конечного продукта.
- Обнаружение загрязнений: Обнаружение и удаление примесей или загрязнений в смоле обеспечивает качество продукции.
- Последовательная обработка: Поддержание единых условий обработки имеет решающее значение для производства ПЭТ с постоянными свойствами.
- Переработка и устойчивое развитие: Включение в производство переработанного ПЭТ (rPET) снижает воздействие на окружающую среду.
Достижения в области производственных технологий и исследований постоянно совершенствуют процесс производства ПЭТ, делая его более эффективным и экологически чистым.

Раздел 4: Применение ПЭТ
Полиэтилентерефталат (ПЭТ) является свидетельством изобретательности материаловедения. Его исключительные свойства позволили найти разнообразное применение в различных отраслях промышленности. В этом разделе мы отправимся в путешествие по некоторым из наиболее известных применений ПЭТ.
4.1 Инновации в упаковке
Замечательное сочетание прозрачности, прочности и барьерных свойств ПЭТ произвело революцию в упаковочной промышленности. Это предпочтительный материал для бесчисленного количества продуктов, в том числе:
- Бутылки для напитков: прозрачность ПЭТ позволяет увидеть содержимое, а его прочность предотвращает поломку, что делает его идеальным для бутылок с водой, газировкой и соком.
- Контейнеры для пищевых продуктов: ПЭТ-контейнеры используются для широкого спектра пищевых продуктов, сохраняя свежесть и безопасность.
- Блистерная упаковка: В фармацевтической промышленности ПЭТ используется для блистерной упаковки, обеспечивая целостность продукта и защиту от несанкционированного доступа.
4.2 Текстиль и одежда
В текстильной промышленности ПЭТ превращается в полиэфирные волокна, используемые для создания одежды и текстиля. Преимущества включают в себя:
- Долговечность: Ткани на основе ПЭТ известны своей долговечностью и подходят для спортивной одежды, уличного снаряжения и автомобильной обивки.
- Сопротивление морщинам: Волокна ПЭТ не мнется, что снижает необходимость в глажке или специальном уходе.
- Стойкость цвета: ПЭТ сохраняет яркие цвета даже после многократных стирок, обеспечивая долговечность одежды.
4.3 Достижения в автомобильной промышленности
Легкие и прочные свойства ПЭТ позволяют найти инновационные применения:
- Компоненты интерьера: материалы на основе ПЭТ используются в покрытиях приборной панели, тканях сидений и ковровых покрытиях, что способствует снижению веса и повышению топливной эффективности.
- Под капотом: ПЭТ используется для изготовления крышек двигателей, компонентов системы охлаждения и корпусов аккумуляторов благодаря своей термостойкости и механической прочности.
4.4 Электроника и упаковка
Электронная промышленность извлекает выгоду из электроизоляционных свойств ПЭТ, используя его для различных применений:
- Изоляция кабеля: ПЭТ изолирует электрические кабели и провода, повышая безопасность.
- Дисплеи: ПЭТ-пленки используются в ЖК- и OLED-дисплеях благодаря их прозрачности и термостойкости.
4.5 Медицина и здравоохранение
В секторе здравоохранения ПЭТ играет решающую роль:
- Медицинское оборудование: Биосовместимость ПЭТ и простота стерилизации делают его предпочтительным выбором для внутривенных пакетов, трубок и протезных имплантатов.
- Фармацевтическая упаковка: ПЭТ используется для фармацевтической упаковки, обеспечивая целостность и безопасность продукта.
4.6 Устойчивые инициативы
Растущая обеспокоенность по поводу экологической устойчивости приводит к увеличению использования переработанного ПЭТ (rPET) в различных областях, что снижает воздействие производства ПЭТ на окружающую среду.

Раздел 5: Устойчивое развитие и ПЭТ
Поскольку наш мир борется с экологическими проблемами, экологичность таких материалов, как полиэтилентерефталат (ПЭТ), становится в центре внимания. В этом разделе мы рассмотрим воздействие ПЭТ на окружающую среду, возможность его вторичной переработки и инновационные методы, которые помогают уменьшить его воздействие на планету.
5.1 Воздействие ПЭТ на окружающую среду
Хотя ПЭТ предлагает множество преимуществ, его производство имеет экологические последствия, в том числе:
- Потребление ресурсов: Производство ПЭТ-смолы требует значительных затрат энергии и сырья, особенно сырой нефти для компонента этиленгликоля.
- Пластиковые отходы: Неправильная утилизация изделий из ПЭТ может привести к образованию пластиковых отходов, которые могут сохраняться в окружающей среде в течение сотен лет.
5.2 Переработка ПЭТ: устойчивое решение
Преимуществом ПЭТ является его возможность вторичной переработки. ПЭТ является одним из наиболее перерабатываемых пластиков в мире благодаря своей чистоте, прозрачности и простоте обработки. Процесс переработки включает в себя несколько основных этапов:
- Коллекция: ПЭТ-продукты, такие как бутылки и контейнеры, собираются из различных источников, включая домашние хозяйства, предприятия и центры переработки.
- Сортировка: Предприятия по переработке используют автоматизированные системы для сортировки ПЭТ от других пластмасс и материалов.
- Очистка: Тщательная очистка удаляет этикетки, крышки и загрязнения с собранных предметов из ПЭТ.
- Измельчение: Очищенный ПЭТ измельчается на мелкие кусочки или хлопья.
- Плавление и реформирование: Эти хлопья плавятся и превращаются в новые продукты из ПЭТ, включая бутылки, одежду и даже ковровые волокна.
Переработанный ПЭТ, часто называемый rPET, экономит энергию, снижает потребление ресурсов и минимизирует объем пластиковых отходов. Использование rPET становится все более распространенным в различных отраслях, способствуя более устойчивой и замкнутой экономике.
5.3 Инициативы по устойчивому ПЭТ
В ответ на растущие экологические проблемы отрасли активно ищут устойчивые альтернативы и методы:
- ПЭТ на биологической основе: Исследователи изучают возможность использования сырья биологического происхождения, такого как этиленгликоль растительного происхождения, чтобы снизить зависимость от ископаемого топлива при производстве ПЭТ.
- Экологичная упаковка: Компании инвестируют в экологически безопасный дизайн упаковки, например, в облегчение бутылок, чтобы сократить использование материалов и выбросы углекислого газа во время транспортировки.
- Общественная осведомленность: Просвещение потребителей о важности переработки и ответственной утилизации является важнейшим аспектом инициатив по устойчивому использованию ПЭТ.
- Расширенная ответственность производителя (EPR): В некоторых регионах реализуются программы EPR, согласно которым производители несут ответственность за переработку и правильную утилизацию изделий из ПЭТ.
5.4 Путь к устойчивому будущему
Полиэтилентерефталат продемонстрировал свою адаптируемость не только как универсальный материал, но и как чемпион в стремлении к устойчивому развитию. Поскольку технологии и практика продолжают развиваться, ПЭТ играет ключевую роль в уменьшении воздействия на окружающую среду.

Раздел 6: ПЭТ в сравнении с другими пластиками
В огромном мире полимеров и пластмасс каждый материал имеет свой набор характеристик и сфер применения. В этом разделе мы сравним полиэтилентерефталат (ПЭТ) с некоторыми другими пластиками, подчеркнув сильные стороны и различия, которые отличают ПЭТ.
6.1 ПЭТ по сравнению с полипропиленом (ПП)
Полипропилен — еще один широко используемый термопласт, часто конкурирующий с ПЭТ:
- Ясность против гибкости: ПЭТ отличается превосходной прозрачностью по сравнению с ПП, что делает его предпочтительным для продукции, где прозрачность важна, например, для бутылок для напитков. ПП, с другой стороны, известен своей гибкостью и устойчивостью к химическим веществам, что делает его подходящим для контейнеров, которые должны выдерживать агрессивное содержимое.
- Возможность вторичной переработки: И ПЭТ, и ПП подлежат вторичной переработке, но прозрачность ПЭТ и совместимость с процессами переработки дали ему преимущество в показателях переработки.
6.2 ПЭТ против полиэтилена (ПЭ)
Полиэтилен является одним из наиболее распространенных пластиков и бывает различных форм:
- Прочность и жесткость: ПЭТ прочнее и жестче, чем большинство видов полиэтилена, что делает его пригодным для применений, требующих долговечности, таких как автомобильные детали и медицинские устройства.
- Прозрачность: Хотя некоторые виды полиэтилена прозрачны, ПЭТ обеспечивает постоянную прозрачность для более широкого спектра продуктов.
6.3 ПЭТ по сравнению с поливинилхлоридом (ПВХ)
Поливинилхлорид известен своей универсальностью и долговечностью:
- Химическая устойчивость: ПВХ превосходит ПЭТ по химической стойкости, что делает его предпочтительным для труб, изоляции проводов и других применений, где воздействие агрессивных химикатов является проблемой.
- Пригодность к вторичной переработке и устойчивое развитие: ПЭТ часто рассматривается как более экологичный вариант из-за более высоких показателей переработки и совместимости с экологически чистыми методами.
6.4 ПЭТ против полистирола (ПС)
Полистирол известен своими изоляционными свойствами и универсальностью:
- Изоляция: Полистирол обладает превосходными теплоизоляционными свойствами, что делает его предпочтительным выбором для одноразовых кофейных чашек и контейнеров для пищевых продуктов, предназначенных для сохранения тепла.
- Проблемы окружающей среды: Полистирол подвергался критике за свое воздействие на окружающую среду, особенно в его неперерабатываемых формах. Возможность вторичной переработки ПЭТ и растущее использование вторичного ПЭТ способствуют его более благоприятному профилю устойчивого развития.
Хотя каждый пластик имеет свои уникальные сильные стороны, сочетание прозрачности, прочности, возможности вторичной переработки и универсальности ПЭТ сделало его отличным выбором для широкого спектра применений. Его адаптируемость к различным отраслям является свидетельством его непреходящего значения в мире полимеров.

Раздел 7: Будущие перспективы ПЭТ
Полиэтилентерефталат (ПЭТ) прошел долгий путь с момента своего появления, постоянно развиваясь, чтобы соответствовать постоянно меняющимся требованиям современной промышленности. Заглядывая в будущее, интересно рассмотреть инновации и тенденции, которые формируют будущее ПЭТ.
7.1 Экологичный ПЭТ
Устойчивое развитие остается на переднем крае индустрии пластмасс, и ПЭТ не является исключением. В ближайшие годы мы можем ожидать увидеть:
- Увеличение переработки: Растущее внимание к вторичной переработке и практикам экономики замкнутого цикла будет продолжать стимулировать использование переработанного ПЭТ (rPET) в различных областях применения, что еще больше снизит воздействие ПЭТ на окружающую среду.
- ПЭТ на биологической основе: Исследователи активно изучают биологическое сырье для производства ПЭТ, стремясь снизить зависимость от ископаемого топлива и уменьшить выбросы углекислого газа.
7.2 Передовые технологии производства
Процессы производства ПЭТ становятся все более сложными и эффективными:
- 3D-печать: ПЭТ находит свое применение в 3D-печати, позволяя создавать сложные объекты индивидуального дизайна — от прототипов до медицинских имплантатов.
- Нанотехнологии: Наноматериалы включаются в ПЭТ для улучшения его свойств, например, для улучшения барьерных свойств в упаковке пищевых продуктов.
7.3 Расширенные функциональные возможности
Инновации стимулируют развитие ПЭТ с расширенными функциональными возможностями:
- Умная упаковка: ПЭТ интегрируется с интеллектуальными технологиями для создания упаковки, которая может контролировать свежесть, отслеживать запасы и даже общаться с потребителями.
- Биоразлагаемый ПЭТ: Исследования биоразлагаемых вариантов ПЭТ продолжаются, предлагая более экологичное решение для одноразовых предметов.
7.4 Легкость и дизайн
Усилия по сокращению использования материалов при сохранении производительности будут продолжены:
- Автомобильная промышленность: Автомобильная промышленность будет все чаще обращаться к ПЭТ и другим легким материалам для повышения эффективности использования топлива и снижения выбросов.
- Дизайн упаковки: ПЭТ-упаковка будет развиваться и станет более эффективной с точки зрения использования материалов, обеспечивая надежную защиту продуктов и минимизируя отходы.
7.5 Выход на новые рынки
ПЭТ исследует неизведанные территории:
- Здравоохранение: Биосовместимость ПЭТ и простота стерилизации приведут к его новому применению в медицинских приборах и хирургических инструментах.
- Аэрокосмическая промышленность: Легкий и прочный характер ПЭТ делает его кандидатом на использование в компонентах аэрокосмической отрасли, особенно в связи с тем, что в отрасли используются экологически чистые материалы.
Будущее полиэтилентерефталата изобилует возможностями. Благодаря постоянным исследованиям, технологическим достижениям и непоколебимому стремлению к устойчивому развитию, ПЭТ готов продолжить свой путь в качестве универсального, адаптируемого и экологически безопасного материала.
Раздел 8: Заключение
В заключение, полиэтилентерефталат — это не просто пластик, это символ человеческой изобретательности и адаптируемости. Путь компании от концепции до ее роли в современном мире материалов является свидетельством человеческих инноваций и стремления к более устойчивому будущему. Продолжая исследовать постоянно растущий потенциал ПЭТ, мы находим вдохновение в его способности развиваться и адаптироваться, формируя мир, в котором материалы отвечают как потребностям человека, так и охране окружающей среды.
Раздел 9: Ссылки
При разработке этого всестороннего исследования полиэтилентерефталата (ПЭТ) мы опирались на обширные знания и исследования. Вот ссылки и источники, которые помогли нам в нашем путешествии:
- Гибсон, И. (2015). Полиэфиры. В Справочнике по биомедицинской инженерии (4-е изд., стр. 1573–1588). ЦРК Пресс.
- ПластикЕвропа. (2021). Пластмассы – Факты 2021. [PDF].Факты о пластике в Европе 2021 г.
- Янссон, О. (2019). Бутылки из полиэтилентерефталата (ПЭТ) как ресурс в циркулярной экономике. [Докторская диссертация, Технологический университет Чалмерса].Исследование Чалмерса: бутылки из полиэтилентерефталата (ПЭТ) как ресурс в экономике замкнутого цикла
- Ракес Х. М., Хабиби Ю., Мурариу М., & Дюбуа, П. (2013). Полилактид (PLA): синтез, свойства и применение. В «Химии зеленых полимеров: биокатализ и материалы II» (стр. 1–68). Американское химическое общество.
- Харпер, Калифорния (2002). Справочник по пластическим процессам. Джон Уайли & Сыновья.
- Раджу, РМ (2016). Полимерная наука и технология: пластмассы, резина, смеси и композиты. ЦРК Пресс.
- Гош, СК (2015). Полимерные композиты, Том 2: Нанокомпозиты. ЦРК Пресс.
- Европейская платформа для ПЭТ-бутылок (EPBP). (2021). ПЭТ полностью пригоден для вторичной переработки.EPBP: ПЭТ полностью пригоден для вторичной переработки
- ПластикЕвропа. (2020). Круговая экономика пластмасс. [PDF].PlasticsEurope: замкнутая экономика для пластмасс
- Агентство по охране окружающей среды США. (2021). Устойчивое управление материалами (SMM) Устойчивое управление материалами.EPA Устойчивое управление материалами (SMM)